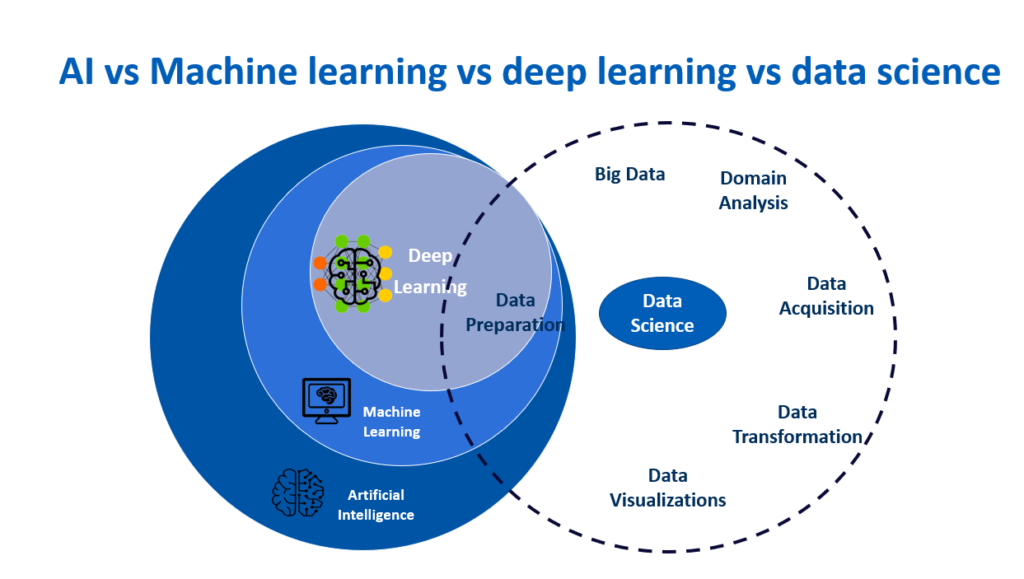
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are two terms that dominate headlines and ignite conversations around technological advancements. While often used interchangeably, they represent distinct, albeit interconnected, facets of the evolving landscape of intelligent machines. This article aims to clear the confusion, delving into the core concepts, key differences, and exciting applications of both AI and ML, offering a clear roadmap for comprehending this future-shaping technology.
AI: The Grand Vision of Thinking Machines
Imagine a machine capable of reasoning, learning, and adapting like a human. That’s the essence of AI, an umbrella term encompassing the development of intelligent agents that emulate human cognitive abilities. From chess-playing machines to self-driving cars, AI encompasses diverse approaches, including:
- Symbolic AI: Employing rules and logic to mimic human reasoning, like expert systems for medical diagnosis.
- Evolutionary AI: Mimicking natural selection to evolve solutions, often used in games and optimization problems.
- Artificial Neural Networks: Inspired by the brain, these interconnected nodes learn by adjusting their weights, powering breakthroughs in speech recognition and image analysis.
AI strives to create machines that understand, reason, and act in the world, tackling complex tasks without explicit programming. However, achieving true “general AI” – machines with human-level understanding and flexibility – remains an elusive goal.
Machine Learning: Learning from Data, Powering AI
Think of machine learning (ML) as the engine driving many AI advancements. It’s a specific technique where algorithms learn from data, improving their performance over time without explicit instructions. Imagine feeding a computer thousands of cat pictures; an ML algorithm can then analyze new images and accurately identify felines it has never seen before.
Here’s how it works:
- Data Acquisition: Feeding the algorithm massive datasets of text, images, or other information.
- Model Training: Exposing the algorithm to these examples, allowing it to identify patterns and relationships.
- Evaluation and Refinement: Testing the model’s performance and adjusting its parameters for better accuracy.
ML algorithms like:
- Decision Trees: Making choices based on a series of questions, used in fraud detection.
- Support Vector Machines: Classifying data into categories, employed in image recognition.
- Deep Learning: Utilizing complex neural networks, achieving breakthroughs in natural language processing.
ML empowers machines to learn and adapt, fueling a wide range of AI applications, from personalized recommendations to medical diagnosis.
Machine Learning vs. AI: Key Differences
While ML forms a crucial part of many AI systems, they are distinct:
| Feature | Machine Learning | Artificial Intelligence |
|---|---|---|
| Goal | Learn from data and improve performance on specific tasks. | Achieve human-like intelligence and reasoning. |
| Methods | Algorithms trained on data (e.g., decision trees, neural networks). | Diverse approaches including logic, rules, and learning. |
| Focus | Specific tasks and data-driven improvement. | Broader goal of mimicking human intelligence. |
| Current State | Well-developed with numerous applications. | Still evolving, with general AI remaining a challenge. |
drive_spreadsheetExport to Sheets
Think of AI as the ambition, and ML as the tool that helps achieve it.
Exciting Applications: Reimagining the World with AI & ML
The real power lies in the synergy between AI and ML. Their combined potential is transforming industries:
- Healthcare: ML algorithms analyze medical scans for early disease detection, while AI systems assist in personalized treatment plans.
- Finance: AI-powered fraud detection systems combat financial crime, while ML personalizes financial products and services.
- Manufacturing: Robots powered by AI and ML improve production efficiency and quality control.
- Climate Change: AI models forecast weather patterns and predict environmental risks, while ML optimizes energy usage and promotes sustainability.
However, responsible development and ethical considerations are crucial. Bias in data can lead to biased algorithms, and transparency in decision-making processes is essential to build trust.
AI and ML : Demystifying the Future
AI and ML are not science fiction fantasies; they are rapidly shaping our present and hold immense potential for the future. By understanding their distinct roles and exciting applications, we can actively participate in shaping this technological revolution, ensuring it benefits all humanity. Remember, AI and ML are tools, and like any tool, their impact depends on the hands that wield them. Let’s work together to ensure they build a brighter, more intelligent future for us all.
Remember: This article is just a starting point. As the field of AI and ML continues to evolve, so too will our understanding of it. Stay curious, keep learning, and join the conversation about the future of intelligent machines!
Frequently Asked Questions: Demystifying AI & ML
Navigating the world of AI and ML can raise many questions. Here are some frequently asked questions with clear answers:
Are AI and robots the same thing?
Not necessarily. While some robots utilize AI, they can also be pre-programmed to perform specific tasks without learning or adapting. AI, on the other hand, can exist without a physical body, like virtual assistants or chatbots.
Will AI take over our jobs?
While automation powered by AI and ML will impact certain jobs, it’s more likely to lead to job creation in new areas requiring human skills like creativity, critical thinking, and social interaction.
How can I learn more about AI and ML?
Numerous online resources, courses, and workshops are available for all levels. Explore platforms like Coursera, edX, and Udacity for beginner-friendly introductions.
Should I be worried about AI becoming too powerful?
Responsible development and ethical considerations are crucial. We must ensure AI serves humanity and is used for good. Open discussions and collaboration are key to shaping a positive future with AI.
Ai and ML: Conclusion
Understanding the nuances of AI and ML empowers us to engage with this technology proactively. Remember, the future is not predetermined. By asking questions, staying informed, and participating in responsible development, we can ensure that AI and ML continue to benefit humanity for generations to come. Let’s embrace the potential of these tools while navigating the challenges responsibly, crafting a brighter future where technological advancements empower and uplift all of us.